Matterhorn
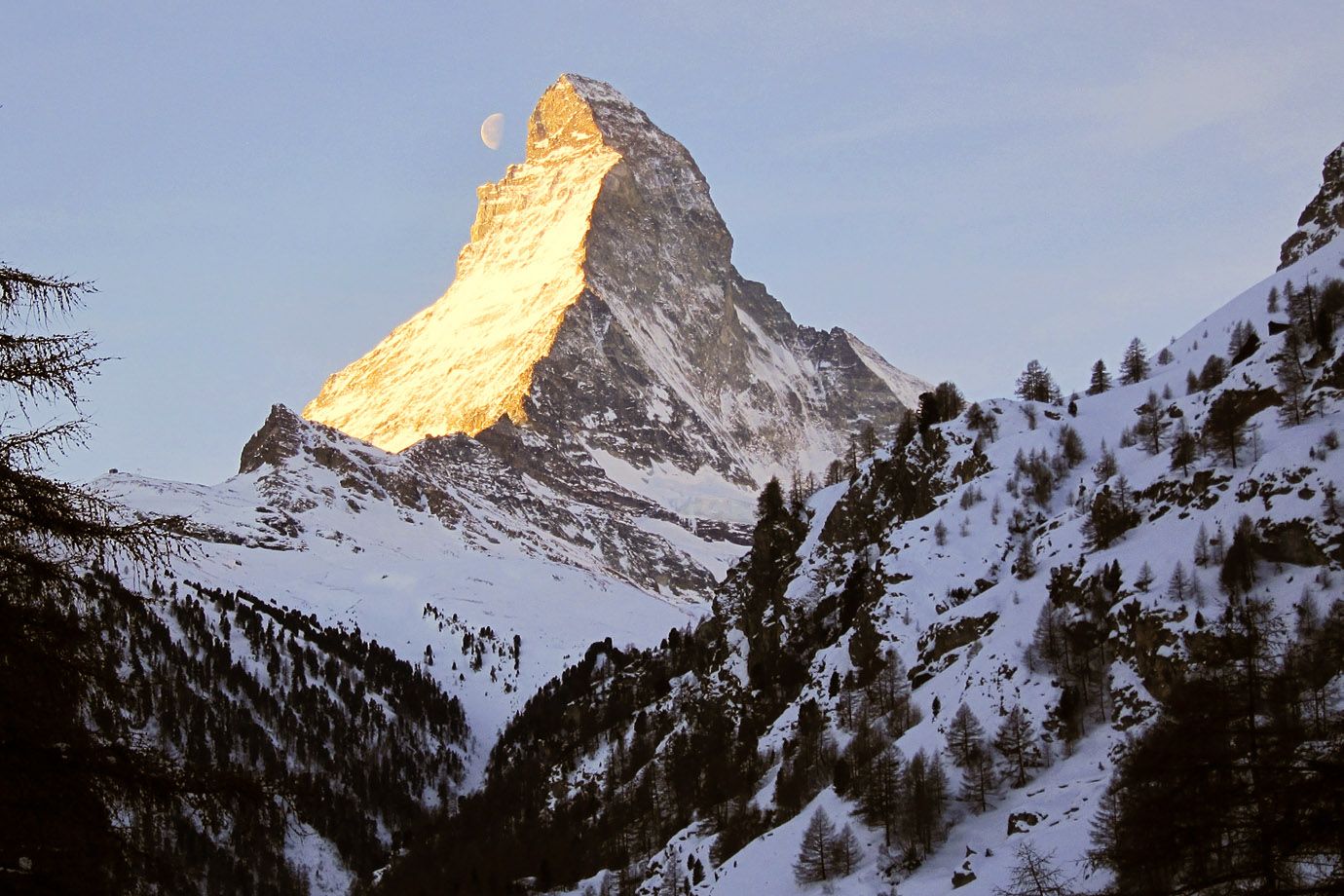
The Matterhorn (German), Monte Cervino (Italian) or Mont Cervin (French), is a mountain in the Pennine Alps on the border between Switzerland and Italy. Its summit is 4,478 metres (14,690 ft) high, making it one of the highest peaks in the Alps. The four steep faces, rising above the surrounding glaciers, face the four compass points.
The Matterhorn is an isolated mountain. Because of its position on the main Alpine watershed and its great height, the Matterhorn is exposed to rapid weather changes. In addition the steep faces of the mountain and its isolated location make it prone to banner clouds formation with the air flowing around and creating vortices, conducting condensation of the air on the lee side.
The Matterhorn has a pyramidal shape with four faces facing the four compass points: the north and east faces overlook, respectively, the Zmutt valley and Gornergrat ridge in Switzerland, the south face (the only one south of the Swiss-Italian border) fronts the resort town of Breuil-Cervinia, and the west face looks towards the mountain of Dent d'Hérens which straddles the border. The north and south faces meet at the summit to form a short east-west ridge.
Source: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matterhorn - 29.11.2011
Moon and Matterhorn
The sun colours the rocks while the moon still stands next to it.