Calcite
Calcite is derived from the German Calcit, a term coined in the 19th century from the Latin word for lime, calx (genitive calcis), with the suffix -ite used to name minerals. It is thus etymologically related to chalk.
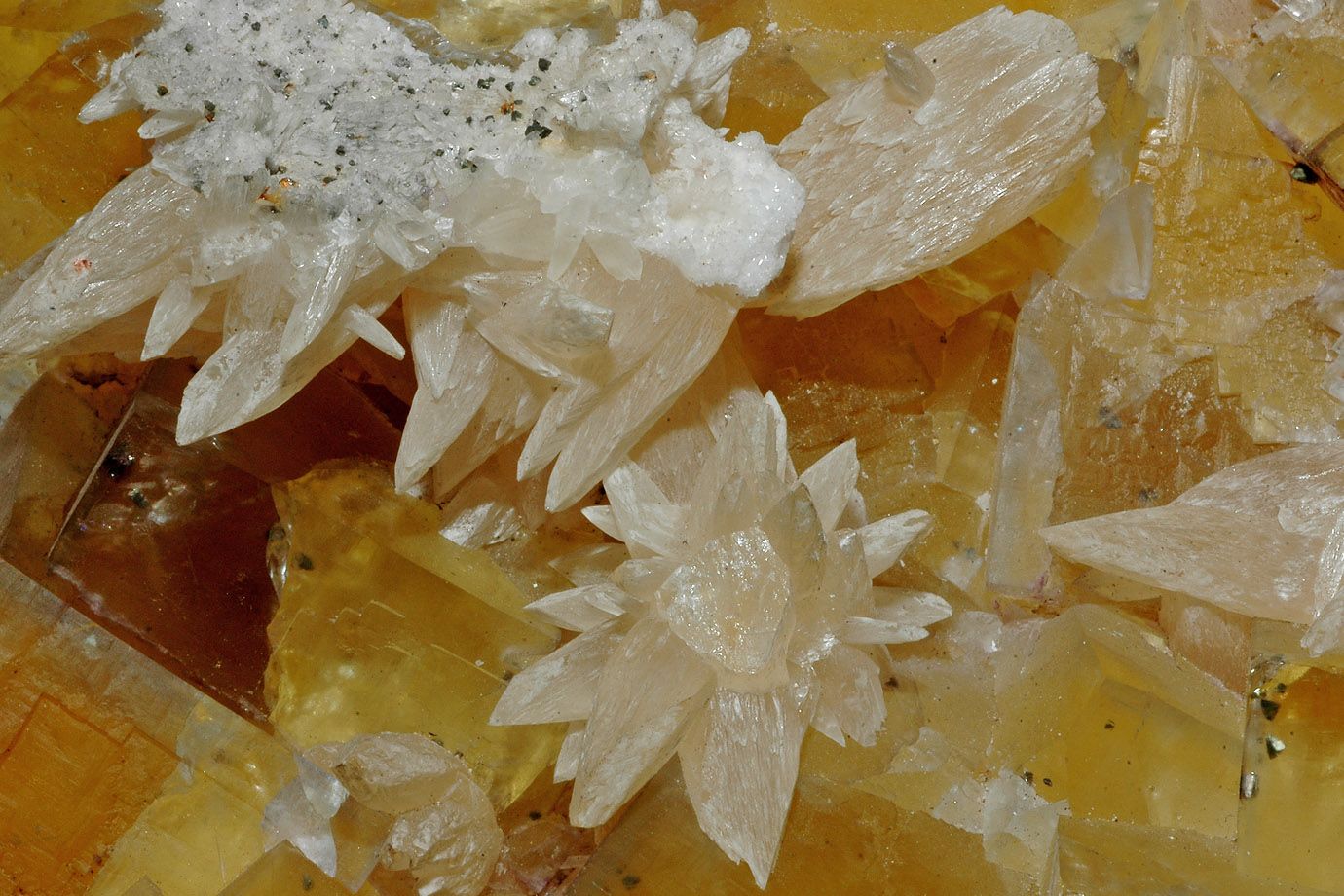
Its form is trigonal-rhombohedral and it shows a remarkable variety of habits including acute to obtuse rhombohedra, tabular forms, prisms, or various scalenohedra. Calcite exhibits several twinning types adding to the variety of observed forms. It may occur as fibrous, granular, lamellar, or compact.
The mineral has a defining Mohs hardness of 3, a specific gravity of 2.71, and its luster is vitreous in crystallized varieties. Color is white or none, though shades of gray, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, brown, or even black can occur when the mineral is charged with impurities.
It is found in spectacular form in the Snowy River Cave of New Mexico. The largest documented single crystal of calcite originated from Iceland, measured 7×7×2 metres and 6×6×3 metres and weighed about 250 tons.
Source: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcite - 23.10.2017
Calcite
This mineral occurs in different crystal forms and in crystal intergrowth - even with other minerals. The photo shows calcite needles on yellow flourite.