Castanea sativa
Castanea sativa is a species of the flowering plant family Fagaceae, the tree and its edible seeds are referred to by several common names such Sweet Chestnut or Marron. Originally native to southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, it is now widely dispersed throughout Europe and parts of Asia, such as the lower Himalayas and other temperate parts of the Indian Subcontinent. The trees are hardy, long lived and well known, especially for its chestnuts which are used as an ingredient in cooking.
Castanea sativa is a medium-sized to large deciduous tree attaining a height of 20–35 m with a trunk often 2 m in diameter. The oblong-lanceolate, boldly toothed leaves are 16–28 cm long and 5–9 cm broad.
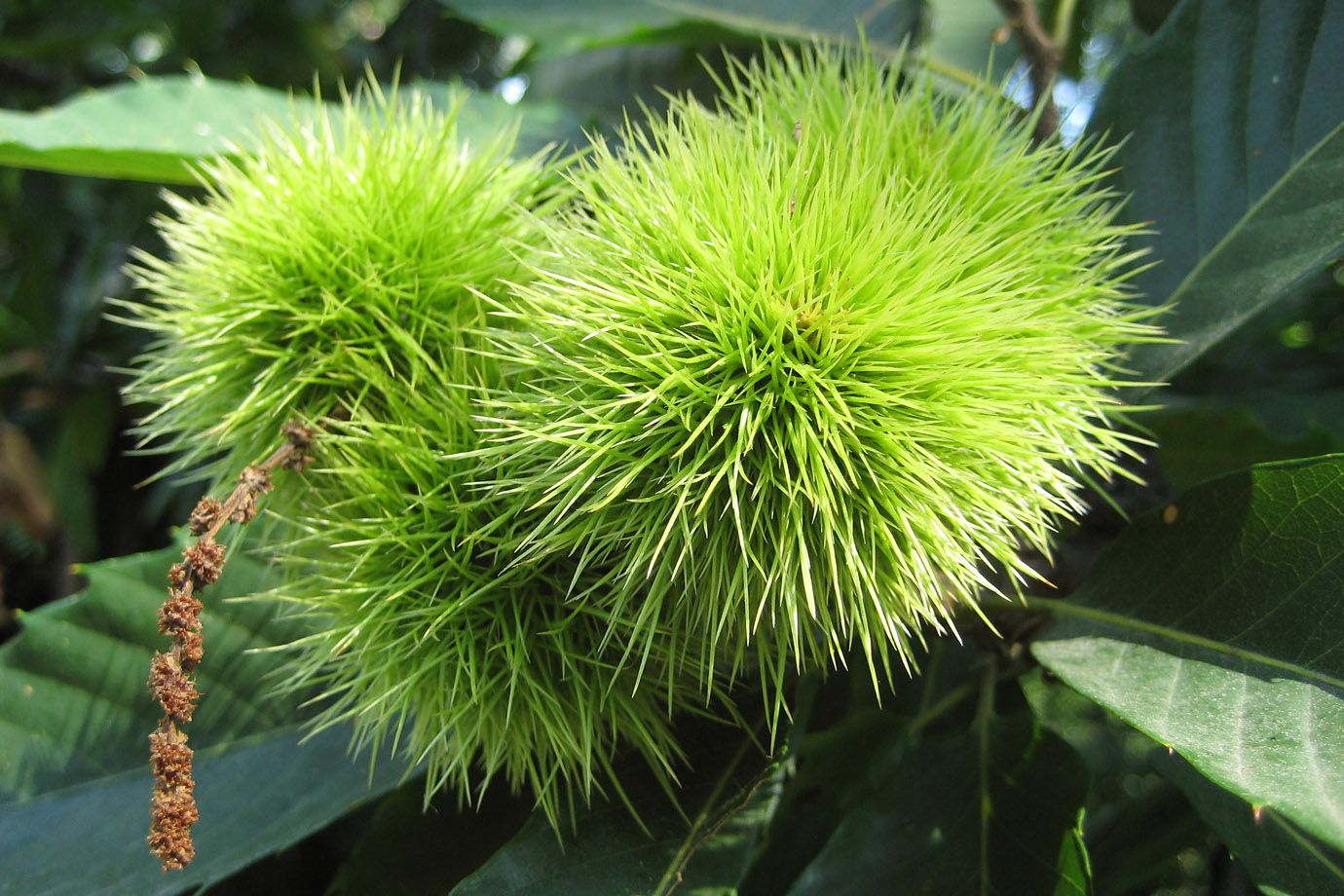
The flowers of both sexes are borne in 10–20 cm long, upright catkins, the male flowers in the upper part and female flowers in the lower part. In the northern hemisphere, they appear in late June to July, and by autumn, the female flowers develop into spiny cupules containing 3-7 brownish nuts that are shed during October.
The tree requires a mild climate and adequate moisture for good growth and a good nut harvest. Its year-growth (but not the rest of the tree) is sensitive to late spring and early autumn frosts, and is intolerant of lime. Under forest conditions it will tolerate moderate shade well.
Source:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Castanea_sativa - 10.12.2011
Castanea sativa
The Castanea sativa and the Aesculus hippocastanum have, mainly with the fruites, a certain similarity, but not only belong to different families, but even to different orders.