Dune
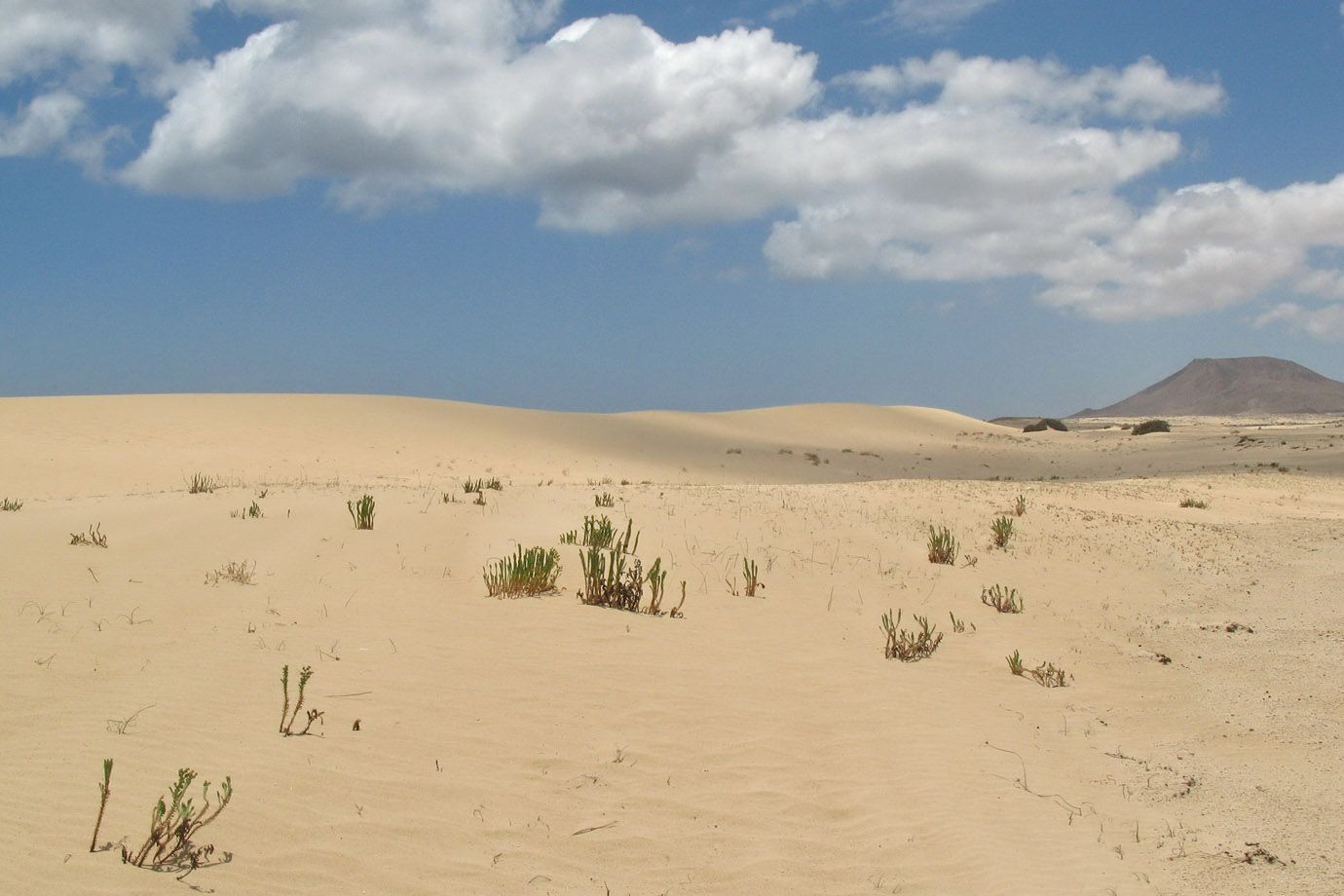
In physical geography, a dune is a hill of sand built by wind. Dunes occur in different forms and sizes, formed by interaction with the wind. Most kinds of dunes are longer on the windward side where the sand is pushed up the dune and have a shorter "slip face" in the lee of the wind. The valley or trough between dunes is called a slack. A "dune field" is an area covered by extensive sand dunes. Large dune fields are known as ergs.
Some coastal areas have one or more sets of dunes running parallel to the shoreline directly inland from the beach. In most cases the dunes are important in protecting the land against potential ravages by storm waves from the sea. Although the most widely distributed dunes are those associated with coastal regions, the largest complexes of dunes are found inland in dry regions and associated with ancient lake or sea beds.
Source: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dune - 05.03.2012
Wandering Dunes
The sand in deserts is able to move as wandering dunes, like the snow in the mountains does as a glacier.