Ice
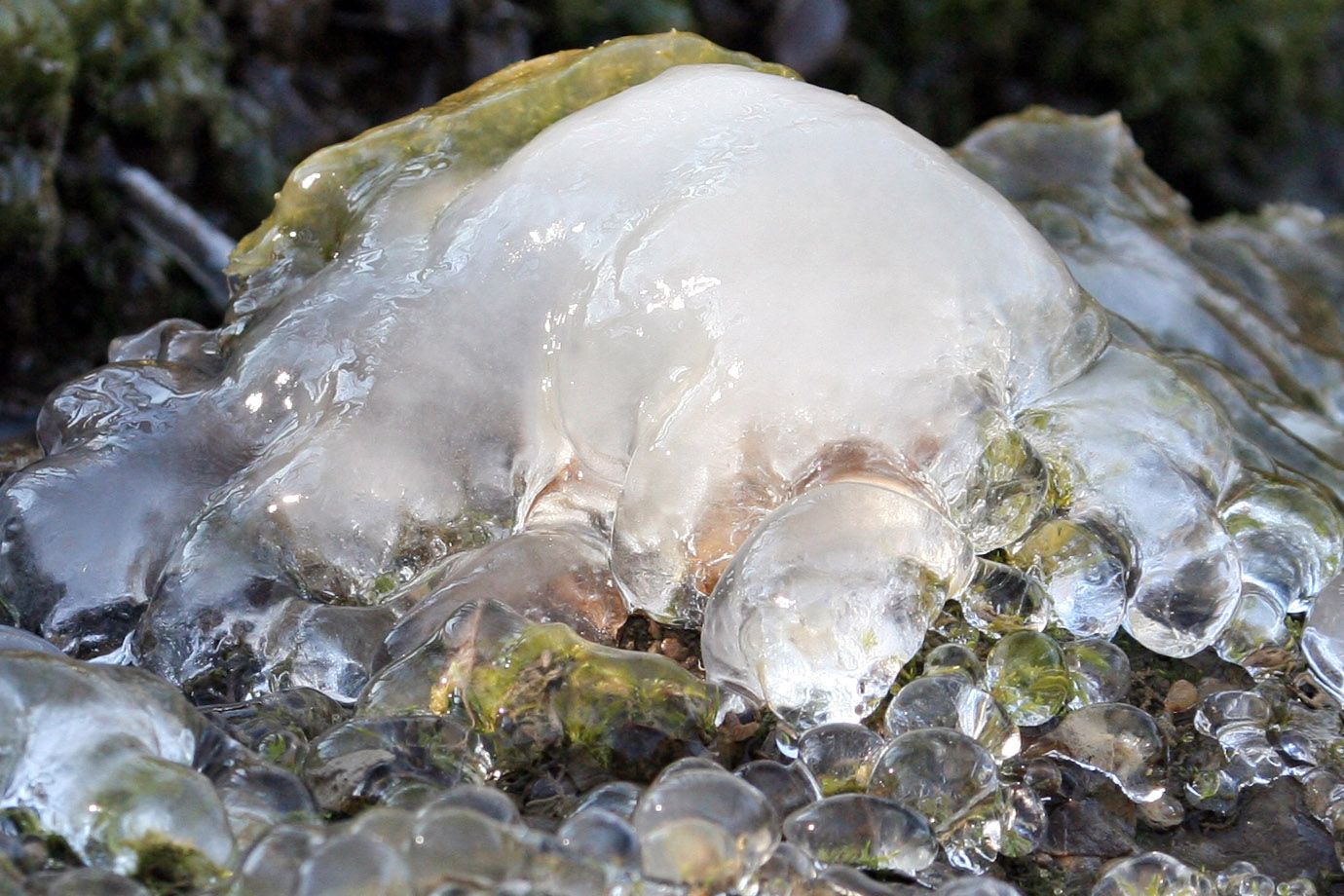
Ice is a solid phase, usually crystalline, of a non-metallic substance that is liquid or gas at room temperature, such as water, carbon dioxide ice (dry ice), ammonia ice, or methane ice. However, the predominant use of the term ice is for water ice, technically restricted to one of the 15 known crystalline phases of water. In non-scientific contexts, the term usually means ice Ih, which is known to be the most abundant of these solid phases. It can appear transparent or opaque bluish-white colour, depending on the presence of impurities or air inclusions. The addition of other materials such as soil may further alter the appearance. he most common phase transition to ice Ih occurs when liquid water is cooled below 0°C at standard atmospheric pressure. It can also deposit from vapour with no intervening liquid phase, such as in the formation of frost. Ice appears in nature in forms of precipitation as varied as snowflakes, hail, icicles, glaciers, pack ice, and entire polar ice caps.
Source: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ice - 25.03.2010
Frozen
The motion and the flow of the water may often still be seen, when it is already temporarily frozen to ice.