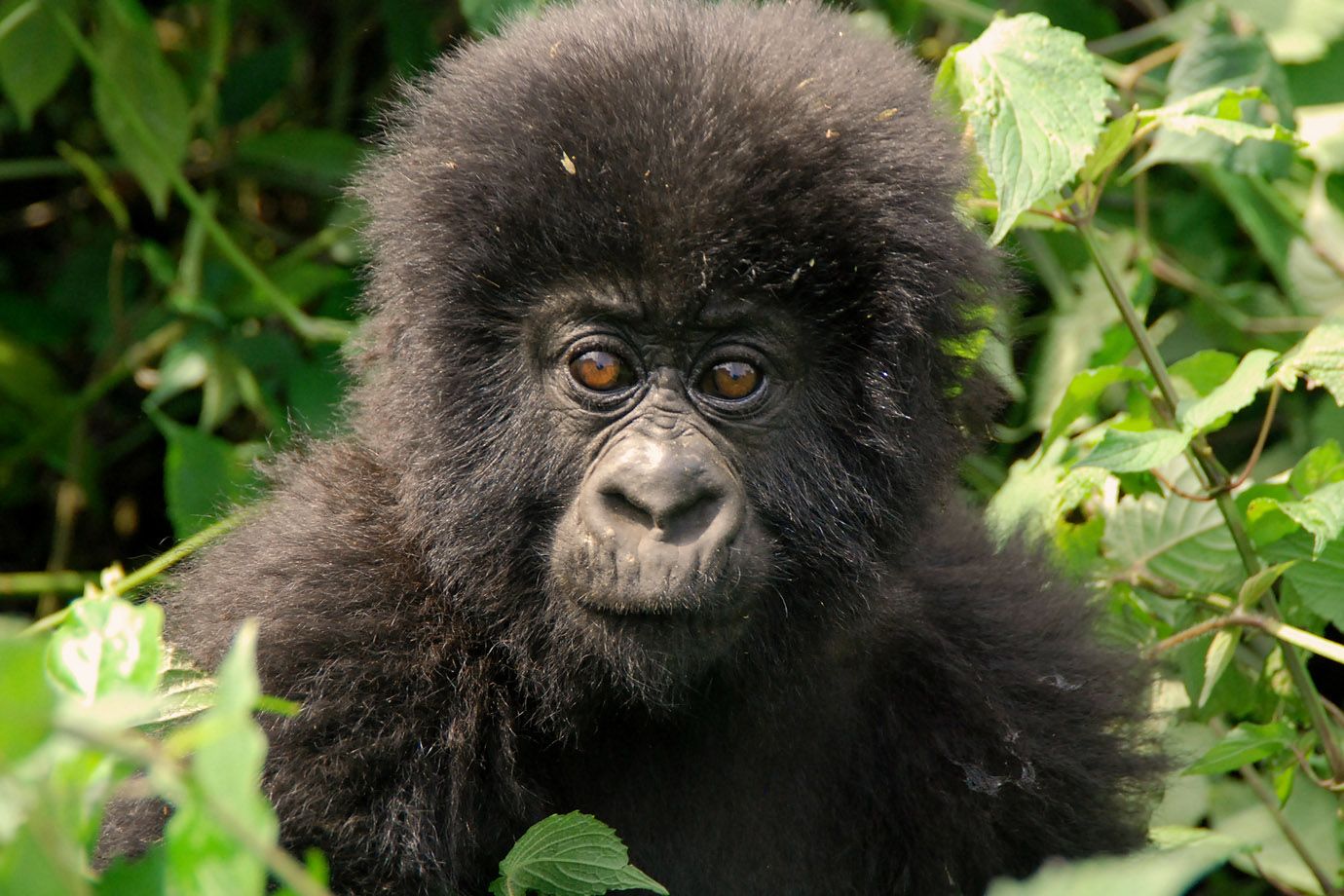
Mountain Gorilla
The Mountain Gorilla is one of the two subspecies of the Eastern Gorilla. There are two populations. One is found in the Virunga volcanic mountains of Central Africa, within three national parks: Mgahinga, in south-west Uganda; Volcanoes, in north-west Rwanda; and Virunga in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. The other is found in Uganda's Bwindi Impenetrable National Park.
The Mountain Gorilla is highly social, and lives in relatively stable, cohesive groups held together by long-term bonds between adult males and females. These groups are nonterritorial; the silverback generally defends his group rather than his territory. 61% of groups are composed of one adult male and a number of females and 36% contain more than one adult male. The remaining gorillas are either lone males or exclusively male groups, usually made up of one mature male and a few younger males. Group sizes vary from five to thirty. A typical group contains: one silverback, who is the group's undisputed leader; one or two blackbacks, who act as sentries; three to four sexually mature females, who are ordinarily bonded to the dominant silverback for life; and from three to six juveniles and infants.
Source: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mountain_Gorilla - 05.05.2010
Mountain Gorilla
This young monkey is one of the last of 700 Mountain Gorillas world-wide.